Java基础教程(全代码解析)
发表时间:2022-03-23来源:网络
字面量:
整数字面量为整型(int)
小数字面量为双精度浮点型(double)
数据类型:
byte short int long float double
接下来代码展示理解
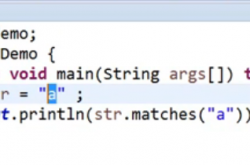
public class Test{ char c = 'a'; switch(c){ case 'b': System.out.println('b'); break; case 'c': System.out.println('c'); break; case 'a': System.out.println('a'); break; default: System.out.println('d'); } } }swith( char byte short int)只允许四种类型
public class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ int score = 90; if(score > 85 && score 75 && score 60 && score 100 || score < 0){ System.out.println("成绩不在正常的范围之内"); } } } for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ System.out.println(i); } public class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ int i = 0; while(i < 10){ System.out.println(i); i++; } } }打印100-200的素数:
class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ for(int i = 100; i < 201; i++){ boolean b = false; for(int j = 2; j < i-1; j++){ int k=i%j; if(k==0){ b=true; } } //如果不是true就打印出素数 if(!b){ System.out.println(i); } } } } public class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ int i = 5; int j = i++ + 5; System.out.println(i); System.out.println(j); } } j=10; i=6; int j = ++i + 5; System.out.println(j); j=11; i=6;&逻辑与
&&短路与
什么是接口(interface)
接口中的方法都是抽象方法,public权限,全是抽象函数,不能生成对象
interface Student{ public void read(); public void write(); } class ChineseStudent implements Student{ //复写 public void read(){ System.out.println("read"); } public void write(){ System.out.println("write"); } } class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ ChineseStudent chinesestudent = new ChineseStudent(); Student student = chinesestudent; student.read(); student.write(); } }接口的基本语法如上
实现接口用implements关键字,一个接口可以实现多个接口,一个接口可以继承多个接口
interface Student{ public void read(); public void write(); } interface Teacher{ public void teach(); public void test(); } class Person implements Student,Teacher{ public void read(){ System.out.println("read"): } public void write(){ System.out.println("write"); } public void teach(){ System.out.println("teach"): } public void test(){ System.out.println("test"): } } class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ Person person = new Person(); Student student = person; student.read(); student.write(); Teacher teacher = person; teacher.teach(); teacher.close(); } } 工厂方法模式: interface Printer{ public void open(); public void close(); public void print(String s); } class Printer1 implements Printer{ public void open(){ System.out.println("printer1 open"); } public void close(){ System.out.println("printer1 close"); } public void print1(String s){ System.out.println("print1"+s); } } class Printer2 implements Printer{ private void clean(){ System.out.println("printer2 clean"); } public void close(){ this.clean(); System.out.println("print2 close"); } public void open(){ System.out.println("print2 open"); } public void print(String s){ System.out.println("print2"+s); } } class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ //根据用户的选择 printer.open(); printer.print("test"); printer.close(); } } 工厂 class PrinterFactory{ public static Printer getPrinter(int flag){ Printer printer = null; //int flag = 0; if(flag == 0){ printer = new printer1(); } else(flag == 1){ printer = new CanonPrinter(); } return printer; } } class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ //Printer gerPrinter(int flag) int flag = 1; Printer printer = PrinterFactory.getPrinter(flag); printer.open(); printer.print("test"); printer.close(); } } Java中的异常 什么是异常? try...catch...finally结构的使用方法 class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int i = 1 / 0; } catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ System.out.println("finally"); } System.out.println(5); } } class Test{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ Thread.sleep(1000); } catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } throw和throws的作用区别: 用代码表示: class Person{ private int age; public void setAge(int age) throws Exception{ if(age上一篇:各种java技术文章汇总整理
下一篇:掌握Java编程技巧,代码重构
知识阅读
软件推荐
更多 >-
 查看
查看皓盘云建最新版下载v9.0 安卓版
53.38MB |商务办公
-
 查看
查看ris云客移动销售系统最新版下载v1.1.25 安卓手机版
42.71M |商务办公
-
 查看
查看粤语翻译帮app下载v1.1.1 安卓版
60.01MB |生活服务
-
 查看
查看人生笔记app官方版下载v1.19.4 安卓版
125.88MB |系统工具
-
 查看
查看萝卜笔记app下载v1.1.6 安卓版
46.29MB |生活服务
-
 查看
查看贯联商户端app下载v6.1.8 安卓版
12.54MB |商务办公
-
 查看
查看jotmo笔记app下载v2.30.0 安卓版
50.06MB |系统工具
-
 查看
查看鑫钜出行共享汽车app下载v1.5.2
44.7M |生活服务