精细篇Java8强大的stream API接口大全(代码优雅之道)
发表时间:2022-03-23来源:网络
Stream API大全
前言一、Stream特点二、Stream实例化方式2.1 通过集合2.2 通过数组2.3 通过Stream的of方法2.4 通过无限流三、Stream的API方法3.1 filter3.2 limit3.3 skip3.4 distinct3.5 map3.6 排序3.7 匹配与查找1、allMatch2、anyMatch3、noneMatch4、findFirst5、findAny6、count7、max8、min3.8 归约3.9 收集 collect总结前言
Java 8 API添加了一个新的抽象称为流Stream,可以让你以一种声明的方式处理数据。
一、Stream特点
stream不存储数据,而是按照特定的规则对数据进行计算,一般会输出结果。stream不会改变数据源,通常情况下会产生一个新的集合或一个值。stream具有延迟执行特性,只有调用终端操作时,中间操作才会执行。二、Stream实例化方式
2.1 通过集合
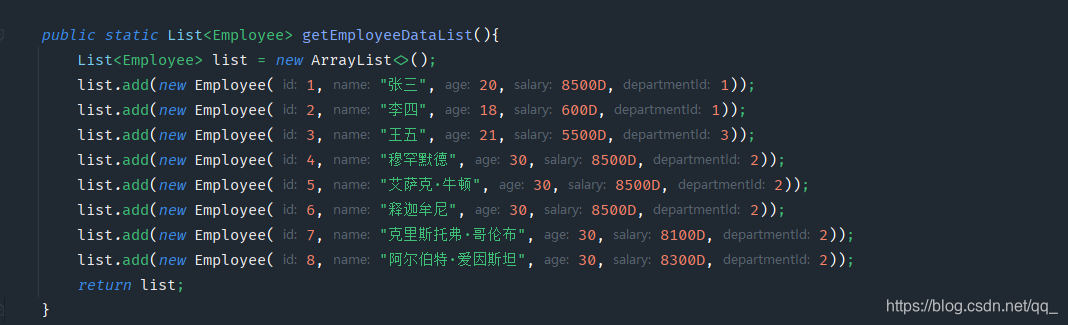
public static List getEmployeeDataList(){ List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(new Employee(1,"张三",20,8500D,1)); list.add(new Employee(2,"李四",18,600D,1)); list.add(new Employee(3,"王五",21,5500D,3)); list.add(new Employee(4,"小白",30,8500D,2)); return list; } public static void main(String[] args) { List employees = getEmployeeDataList(); // 返回一个顺序流 (按照集合顺序获取) Stream stream = employees.stream(); // 返回一个并行流 (类似于线程去获取数据,无序) Stream parallelStream = employees.parallelStream(); }2.2 通过数组
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6}; IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(arr); Employee e1 = new Employee(1, "张三", 20, 8500D, 1); Employee e2 = new Employee(2, "李四", 18, 600D, 1); Employee[] employees = new Employee[]{e1,e2}; Stream stream = Arrays.stream(employees); }2.3 通过Stream的of方法
public static void main(String[] args) { Stream integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); }2.4 通过无限流
public static void main(String[] args) { // 生成偶数 Stream.iterate(0,t->t+2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); // 10个随机数 Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); }三、Stream的API方法
3.1 filter
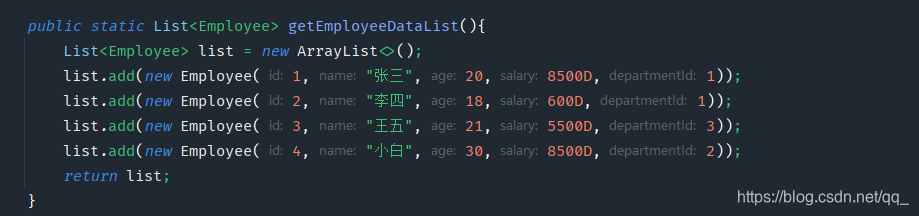
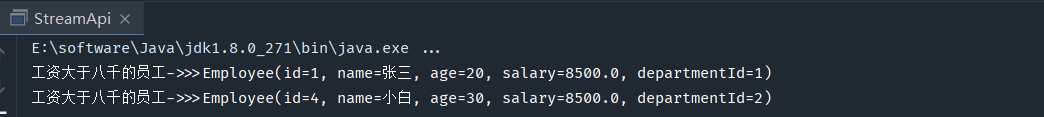
筛选工资大于8000的员工:
3.2 limit
输出集合元素数量
public static void main(String[] args) { List employees = getEmployeeDataList(); employees.stream().limit(3).forEach(t-> System.out.println("输出集合元素数量->>>"+t)); }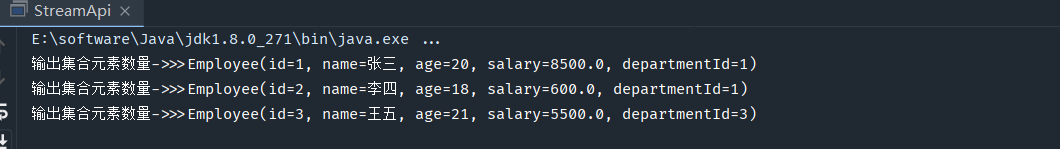
3.3 skip
过滤掉前面的2个元素
public static void main(String[] args) { List employees = getEmployeeDataList(); employees.stream().skip(2).forEach(t-> System.out.println("过滤掉前面的2个元素->>>"+t)); }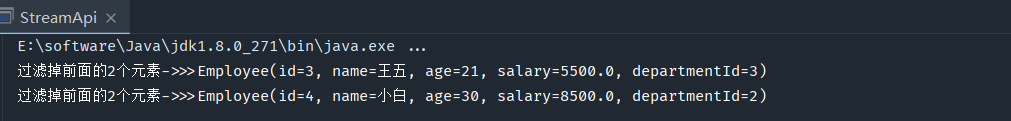
3.4 distinct
集合去重
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(new Employee(1,"张三",20,8500D,1)); list.add(new Employee(1,"张三",20,8500D,1)); list.add(new Employee(1,"张三",20,8500D,1)); list.add(new Employee(1,"张三",20,8500D,1)); list.add(new Employee(1,"张三",20,8500D,1)); list.stream().distinct().forEach(t-> System.out.println("集合去重->>>"+t)); }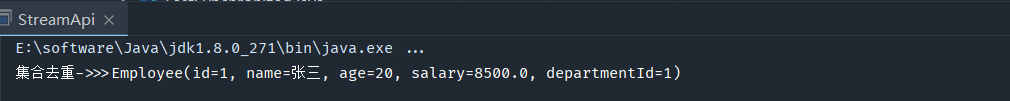
3.5 map
大小写转换
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d"); list.stream().map(str -> str.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT)).forEach(t-> System.out.println("大小写转换->>>"+t)); }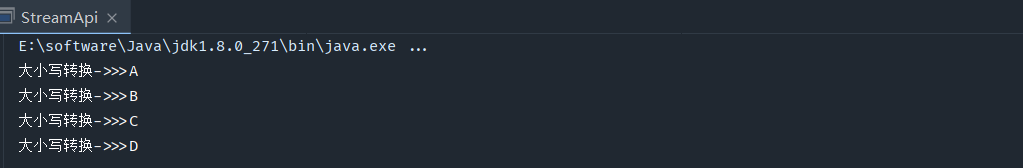
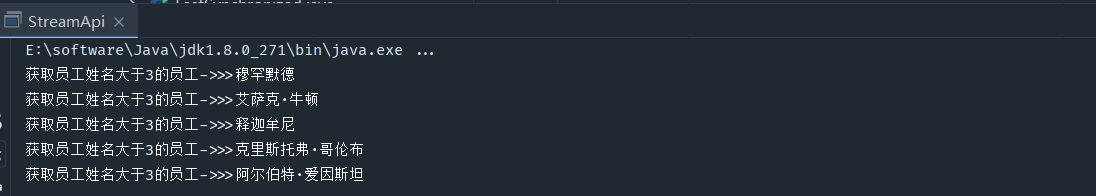
获取员工姓名大于3的员工姓名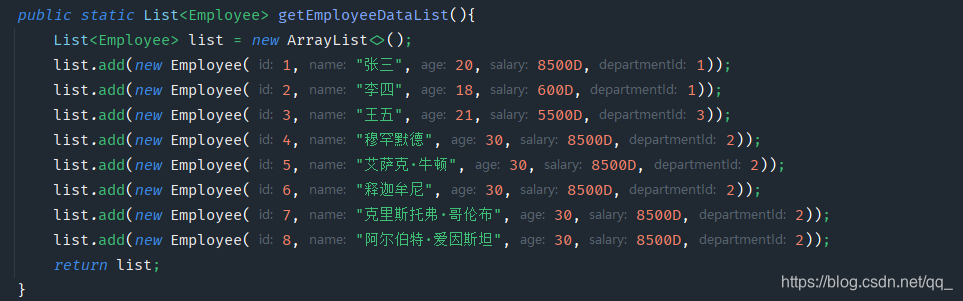
3.6 排序
先按照年龄从小到大排序,当年龄一样的时候,按照工资高低进行排序
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); list.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->{ int age = Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge()); if(age != 0){ return age; }else { return Double.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()); } }).forEach(System.out::println); }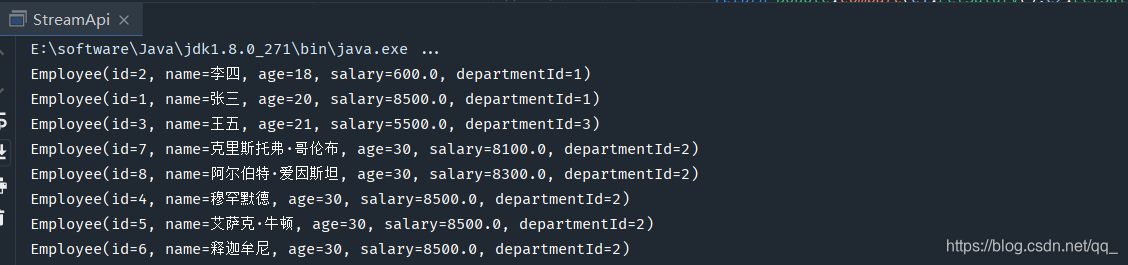
3.7 匹配与查找
1、allMatch
allMatch:检查是否匹配所有元素
判断员工年龄是否都大于18岁
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); boolean allMatch = list.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 18); System.out.println(allMatch); } 全部满足返回 true 、否则返回false2、anyMatch
anyMatch:检查是否至少匹配一个元素
是否存在有员工工资大于8000的
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); boolean anyMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getSalary() > 8000); System.out.println(anyMatch); } 存在一个元素条件满足即可返回true3、noneMatch
noneMatch:检查是否没有匹配的元素
查询是否有姓张的员工
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); boolean noneMatch = list.stream().noneMatch(employee -> employee.getName().startsWith("张")); System.out.println(noneMatch); } 返回false,说明有,否则没有4、findFirst
findFirst:返回第一个元素
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); Optional first = list.stream().findFirst(); System.out.println(first); }5、findAny
findAny:返回当前流中的任意元素
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); Optional first = list.parallelStream().findAny(); System.out.println(first); }6、count
count:返回流中元素的总个数
查询员工工资大于8000的人数
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); long count = list.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getSalary() > 8000).count(); System.out.println(count); }7、max
max:返回流中的最大值
查询最高的员工工资
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); Stream doubleStream = list.stream().map(employee -> employee.getSalary()); Optional max = doubleStream.max(Double::compare); System.out.println(max); }8、min
min:返回流中的最小值
查询最低的员工工资
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); Optional min = list.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())); System.out.println(min); }3.8 归约
reduce:可以将流中的元素反复结合起来,得到一个值
求出1到10的总和
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10); Integer reduce = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum); System.out.println(reduce); } reduce的第一个参数0:代表初始值。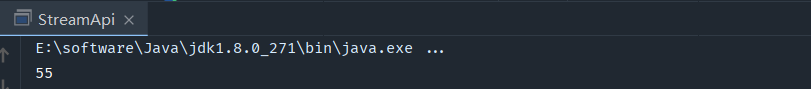
计算公司中所有员工的总和
3.9 收集 collect
查找工资大于8000的员工,返回一个list或者set
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); List collect = list.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getSalary() > 8000).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(collect); } public static void main(String[] args) { List list = getEmployeeDataList(); Set collect = list.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getSalary() > 8000).collect(Collectors.toSet()); System.out.println(collect); }总结
完结,好了,以上就是全部内容,能坚持看到这里,你一定会有收获,只要反复的练习一定能写出优雅的stream流,后面的文章我们会继续扩展其他的接口实现。
知识阅读
软件推荐
更多 >-
 查看
查看皓盘云建最新版下载v9.0 安卓版
53.38MB |商务办公
-
 查看
查看ris云客移动销售系统最新版下载v1.1.25 安卓手机版
42.71M |商务办公
-
 查看
查看粤语翻译帮app下载v1.1.1 安卓版
60.01MB |生活服务
-
 查看
查看人生笔记app官方版下载v1.19.4 安卓版
125.88MB |系统工具
-
 查看
查看萝卜笔记app下载v1.1.6 安卓版
46.29MB |生活服务
-
 查看
查看贯联商户端app下载v6.1.8 安卓版
12.54MB |商务办公
-
 查看
查看jotmo笔记app下载v2.30.0 安卓版
50.06MB |系统工具
-
 查看
查看鑫钜出行共享汽车app下载v1.5.2
44.7M |生活服务