无锁编程基础与代码实现
发表时间:2022-03-25来源:网络
什么是无锁编程
无锁编程,即访问多线程共享数据时,不加/解锁。
这里的“锁”并不特指mutex,还包括使用semaphore、条件变量、信号等构造出的线程挂起等待机制。甚至我们不使用这些操作系统提供的支撑,也可以写出一个“有锁”的接口(在接口中死等某个变量,类似spinlock)。
无锁操作,通常被抽象成方法、接口。比如说针对一个无锁的队列,pop、push就是它的无锁操作。Herlihy & Shavit 给无锁操作给出一个简洁的定义:调用无锁操作时,无论如何都不应该产生任何阻塞。
无锁编程有如下几点优势:
加锁,等待锁涉及系统调用,影响性能。无锁编程没有这部分的性能损耗。不会产生死锁支撑无锁编程的系统算法与接口
RMW原子操作
这里先介绍RMW原子操作,因为这是支撑各类无锁编程算法的基础。
原子操作的想必大家都熟知,它是指不会被线程调度机制打断的操作;这种操作一旦开始,就一直运行到结束,中间不会有任何上下文切换。
RMW(read-modify-write)原子操作,是指把“读-改-写”三步指令合并到一个原子操作里。例如以下两例,实现数的原子性增减
Win32中的_InterlockedIncrementIOS中的OSAtomicAdd32RMW原子操作需要CPU的支撑,当前各类主流的CPU都提供了类似的功能。
CAS
CAS(compare-and-swap)是一种RMW原子操作,它将以下操作封装在一个原子操作里:
读变量*p对比*p与变量old如果*p与old不相同,不做任何操作。如果*p与old相同,将另一变量new赋值给*p伪代码如下:
function cas(p: pointer to int, old: int, new: int) is if *p ≠ old return false *p ← new return true在实际应用中,CAS函数常常返回*p的当前值。例如,想用CAS构造一个栈的push和pop,伪代码如下:
push(node): curr := head old := curr node->next = curr while (old != (curr = CAS(&head, curr, node))) { old = curr node->next = curr } pop(): curr := head old := curr next = curr->next while (old != (curr = CAS(&head, curr, next))) { old = curr next = curr->next } return currABA问题
CAS算法有一个缺陷,就是会产生ABA问题。ABA问题是指,在执行旧值缓存到本地局部变量和CAS操作之间,线程被切换走,旧值被修改了两次以上,恰好与原旧值相同。cas函数误认为数据没有发生变化,而实际上,数据已经与原来不一样了,
有以上的pop函数为例,pop函数中,next = curr->next 和 while之间,线程被切换走,然后其他线程先把A弹出,又把B弹出,然后又把A压入,栈变成 了A --> C,此时head还是指向A,cas判断可以做交换,把head指向next,即head指向了B。但是此时,B已经不在队列里了。
ABA问题,通常通过添加操作计数来解决。cas中,除了对比*p与变量old外,还需要对比操作计数是否改变。如果值和操作计数都没有改变,才算cas成功,才可以给*p赋于新值。
内存屏障(Memory Barrier)
首先要了解内存乱序:程序在运行时内存实际的访问顺序和程序代码编写的访问顺序不一定一致,这就是内存乱序访问。内存乱序访问行为出现的理由是为了提升程序运行时的性能。在这篇文章中写得很清楚,不再缀述。
很多时候,编译器和 CPU 引起内存乱序访问不会带来什么问题,但一些特殊情况下,程序逻辑的正确性依赖于内存访问顺序,这时候内存乱序访问会带来逻辑上的错误,例如:
// thread 1 while (!ok); do(x); // thread 2 x = 42; ok = 1;此段代码中,ok 初始化为 0,线程 1 等待 ok 被设置为 1 后执行 do 函数。假如说,线程 2 对内存的写操作乱序执行,也就是 x 赋值后于 ok 赋值完成,那么 do 函数接受的实参就很可能出乎程序员的意料,不为 42。
很显然,无锁编程中,CAS及其前后的操作,是强依赖于内存访问的顺序性的。
内存屏障(Memory Barrier),就是为了解决内存乱序的问题。内存屏障接口的之前的程序,可以保证在内存屏障接口之后的程序之前运行。上例中的thread 2可以这样修改:
x = 42; smp_mb(); ok = 1;这样即可保证以上程序运行的正确性。
Linux环境中的无锁编程
此节准备以无锁的机制实现一套队列的入队和出队操作。
接口准备
C语言在C11的标准中,加入了原子操作的标准头文件stdatomic.h,这为我们的无锁编程提供了很大的方便。C11的gcc 4.7及以上版本中支持,因此我们需要准备4.7版本以上的gcc。
C11为我们提供了一组封装好的CAS接口:(https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/atomic/atomic_compare_exchange)
_Bool atomic_compare_exchange_strong( volatile A* obj, C* expected, C desired ); _Bool atomic_compare_exchange_weak( volatile A *obj, C* expected, C desired );这一组CAS接口,比较*obj与*expected是否相等,如果相等,则将*desired赋值给*obj,并返回true;否则返回false。也就是“原子地”执行以下逻辑。
if (memcmp(obj, expected, sizeof *obj) == 0) { memcpy(obj, &desired, sizeof *obj); return true; } else { memcpy(expected, obj, sizeof *obj); return false; }这一组接口有strong和weak两个版本。
weak:即使*obj == *expected,有时会“虚假地”返回false。带来的好处是有更高的性能。strong:返回值完全取决于*obj与*expected是否相等。简要设计
无锁队列的数据结构如下图所示。
设计struct lf_queue_head用于存储队头,队尾,它的node成员,分别指向队头和队尾。struct lf_queue_node表示队列节点,其中包含info子成员,用于原子操作。info.next指向tail方向的下一节点。struct lf_queue_node和struct lf_queue_head都有aba成员,用于操作计数统计以避免ABA问题。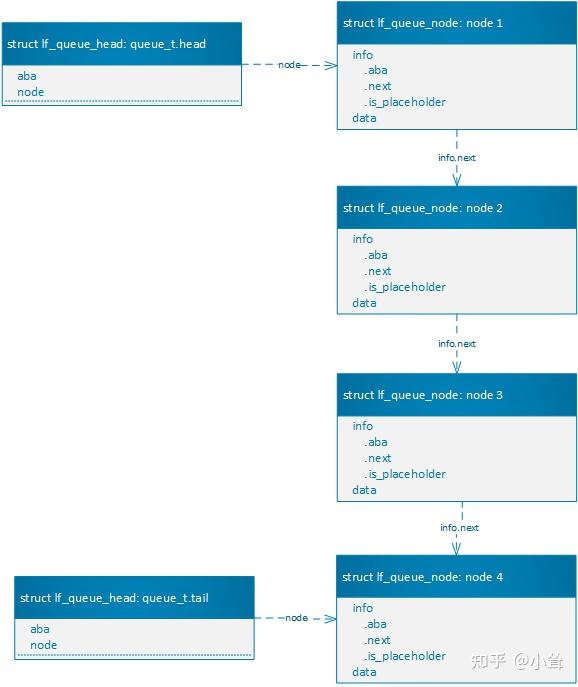
入队操作
新节点创建好之后,执行两个CAS:
将队头node的next指针指向新加入的节点。将queue_t.tail.node队尾指针指向新加入的节点出队操作
执行一个CAS:
把quque_t.head.node队头指针,指向第二个节点队头指针原来指向的节点,即是出队的节点。
占位符节点(placeholder)
为了简化设计,队列中始终保持有一个节点。如果要dequeue最后一个节点时,需要多enqueue一个节点,以便将那个期望的节点“顶出”。这个多enqueue的节点,就是占位符节点。
enqueue一个新节点时,如果队列中有占位符节点。会自动将其dequeue,上层业务不感知占位符节点。
代码实现
lock_free_queue.h
#ifndef _LF_QUEUE_H#define _LF_QUEUE_H #include #include #include #include #include #define LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN (512) struct lf_queue_node_info { struct lf_queue_node *next; bool is_placeholder; uintptr_t aba; }; struct lf_queue_node { _Atomic struct lf_queue_node_info info; char data[LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN]; }; /* queue head and tail */struct lf_queue_head { uintptr_t aba; struct lf_queue_node *node; }; typedef struct { _Atomic struct lf_queue_head head, tail; _Atomic size_t size; } queue_t; int lf_queue_init(queue_t *queue); int lf_queue_enqueue(queue_t *queue, char *data, size_t data_len); int lf_queue_dequeue(queue_t *queue, char *data, size_t data_len); #endif /* #ifndef _LF_QUEUE_H */lock_free_queue.c:
#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include "lock_free_queue.h" #define LFQ_LOG_ERROR printf#define LFQ_LOG_INFO printf #define PLACEHOLDER_DATA 0xee int lf_queue_init(queue_t *queue){ struct lf_queue_head head_init; struct lf_queue_node *init_node; struct lf_queue_node_info info = {NULL, true, 0}; if (queue == NULL) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("queue is NULL\n"); return -1; } init_node = (struct lf_queue_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct lf_queue_node)); if (init_node == NULL) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("fail to malloc.\n"); return -1; } memset(init_node->data, PLACEHOLDER_DATA, sizeof(init_node->data)); init_node->info = ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(info); head_init.aba = 0; head_init.node = init_node; queue->head = ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(head_init); queue->tail = ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(head_init); queue->size = ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(0); LFQ_LOG_INFO("queue %p is initialized\n", queue); return 0; } static int lf_queue_enqueue_inner(queue_t *queue, char *data, size_t data_len, bool enqueue_placeholder, bool check_head_placeholder){ struct lf_queue_node *new_node, *null_node = NULL; struct lf_queue_head new_tail, new_head, tmp_tail, tmp_head; struct lf_queue_node_info new_info, tmp_info; if (queue == NULL) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("queue is NULL\n"); return -1; } if (data_len > LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("datalen is %lu, max length is %d\n", data_len, LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN); return -1; } new_node = (struct lf_queue_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct lf_queue_node)); if (new_node == NULL) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("fail to malloc.\n"); return -1; } if (!enqueue_placeholder) { memcpy(new_node->data, data, data_len); /* placeholder does not have data */ } new_info.aba = 0; new_info.next = NULL; new_info.is_placeholder = enqueue_placeholder; new_node->info = ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(new_info); do { do { do { tmp_tail = atomic_load(&queue->tail); tmp_info = atomic_load(&tmp_tail.node->info); } while(tmp_info.next != NULL); new_info.aba = tmp_info.aba + 1; new_info.next = new_node; new_info.is_placeholder = tmp_info.is_placeholder; } while(!atomic_compare_exchange_weak(&tmp_tail.node->info, &tmp_info, new_info)); new_tail.aba = tmp_tail.aba + 1; new_tail.node = new_node; /* if head is placeholder, dequeue it */ if (!check_head_placeholder) { continue; } do { tmp_head = atomic_load(&queue->head); tmp_info = atomic_load(&tmp_head.node->info); if (!tmp_info.is_placeholder) { break; } LFQ_LOG_INFO("placeholder in head is found while enqueue, dequeue the head placeholder.\n"); new_head.node = tmp_info.next; new_head.aba = tmp_head.aba + 1; } while(!atomic_compare_exchange_weak(&queue->head, &tmp_head, new_head)); } while(!atomic_compare_exchange_weak(&queue->tail, &tmp_tail, new_tail)); if (enqueue_placeholder) { LFQ_LOG_INFO("enqueue placeholder.\n"); } else { LFQ_LOG_INFO("enqueue data: %d %d %d %d %d %d, aba: %"PRIuPTR"\n", data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3], data[4], data[5], new_tail.aba); } return 0; } int lf_queue_enqueue(queue_t *queue, char *data, size_t data_len){ return lf_queue_enqueue_inner(queue, data, data_len, false, true); } /* enqueue an placeholder node to push-out previous node */static int lf_queue_enqueue_placeholder_data(queue_t *queue){ char data[LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN]; int ret; memset(data, PLACEHOLDER_DATA, sizeof(data)); ret = lf_queue_enqueue_inner(queue, data, LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN, true, false); if (ret != 0) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("fail to equeue empty data.\n"); return -1; } LFQ_LOG_INFO("enqueue placeholder node.\n"); return 0; } int lf_queue_dequeue(queue_t *queue, char *data, size_t data_len){ struct lf_queue_head new_head, tmp_head; struct lf_queue_node_info tmp_info; int ret; if (queue == NULL) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("queue is NULL\n"); return -1; } if (data_len > LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("datalen is %lu, max length is %d\n", data_len, LF_QUEUE_DATA_LEN); return -1; } do { tmp_head = atomic_load(&queue->head); tmp_info = atomic_load(&tmp_head.node->info); while (tmp_info.next == NULL) { if (tmp_info.is_placeholder) { LFQ_LOG_INFO("only node is placeholder, empty queue\n"); return -1; } LFQ_LOG_INFO("last node, enqueue an placeholder node to push-out the node.\n"); /* always maintain one node in queue, enqueue a placeholder to push-out the node */ ret = lf_queue_enqueue_placeholder_data(queue); if (ret != 0) { LFQ_LOG_ERROR("fail to equeue placeholder data.\n"); return -1; } tmp_head = atomic_load(&queue->head); tmp_info = atomic_load(&tmp_head.node->info); } new_head.node = tmp_info.next; new_head.aba = tmp_head.aba + 1; } while(!atomic_compare_exchange_weak(&queue->head, &tmp_head, new_head)); memcpy(data, tmp_head.node->data, data_len); free(tmp_head.node); if (tmp_info.is_placeholder) { LFQ_LOG_INFO("dequeue placeholder.\n"); } else { LFQ_LOG_INFO("dequeue data: %d %d %d %d %d %d, aba: %"PRIuPTR"\n", data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3], data[4], data[5], tmp_head.aba); } return 0; }以上代码仍然存在一些缺陷,有进一步改进的空间:
严格来说,这段代码仍然不是lock-free的,因为malloc等内存申请操作可能不是lock-free的。为了保证队列的入队和出队是完全无锁的,我们在初始化时,把所需的内存全部申请好。并用lock-free的方式来管理这些内存块。